Python Data Science Tutorials
You use Python to explore, analyze, and visualize data with pandas, NumPy, SciPy, and Jupyter. Create clear charts with Matplotlib and Seaborn, clean messy datasets, and write tests so analyses are repeatable. Work through practical tasks like feature engineering, time series, and text processing while using virtual environments to keep tooling reliable.
Join Now: Click here to join the Real Python Newsletter and you’ll never miss another Python tutorial, course, or news update.
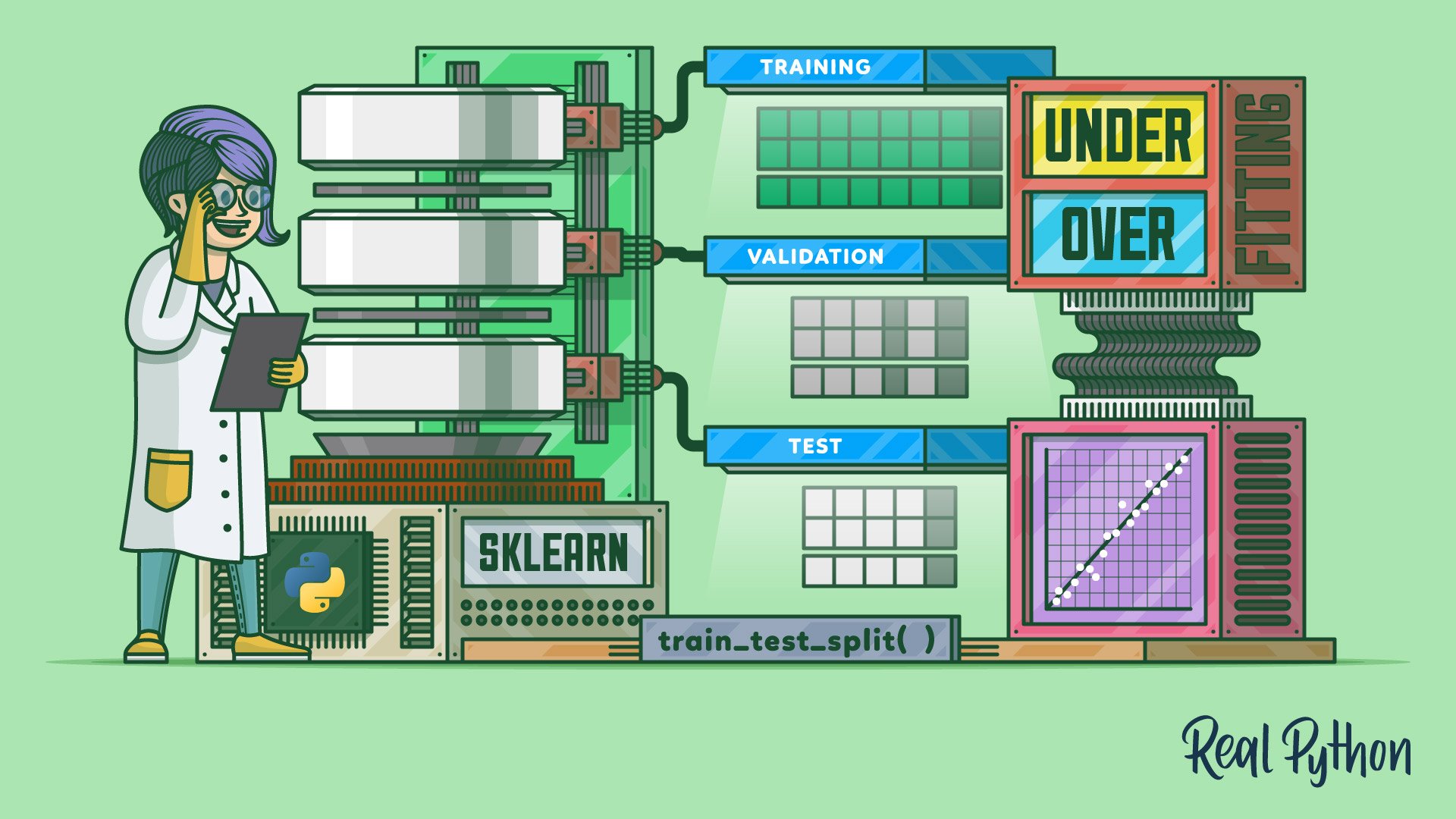
When you are ready to model, apply scikit-learn for classification, regression, clustering, and pipelines. For deep learning, train with Keras, TensorFlow, or PyTorch and track results. Scale workloads with Dask, store data in SQLite, PostgreSQL, and deploy predictions with FastAPI and Docker.
Browse all resources below, or commit to a guided Learning Path with progress tracking:
Learning Path
Data Science With Python Core Skills
20 Resources ⋅ Skills: Pandas, NumPy, Data Cleaning, Data Visualization, Statistics
Learning Path
Math for Data Science
5 Resources ⋅ Skills: Statistics, Correlation, Linear Regression, Logistic Regression, NumPy, SciPy, pandas, Gradient Descent
Learning Path
pandas for Data Science
15 Resources ⋅ Skills: pandas, Data Science, Data Visualization, DataFrame, GroupBy, Data Cleaning
Install pandas with python -m pip install pandas. Read files using pd.read_csv() or pd.read_parquet(), inspect with df.info() and df.describe(), and summarize with groupby() and agg().
Use scikit-learn for classical ML tasks and pipelines. Choose TensorFlow or PyTorch for deep learning, and consider XGBoost for strong tabular baselines.
Start with Matplotlib for full control and Seaborn for quick, statistical plots. Set styles, labels, and legends, and export figures with plt.savefig() for reports and dashboards.
Use Dask for pandas-like processing on larger-than-memory data, or PySpark when you need a cluster. For single-machine workflows, stream with chunksize, downcast dtypes, and store data as Parquet.
Serialize the model with joblib.dump(), load it in a FastAPI app, and expose a POST /predict endpoint. Run with Uvicorn or behind Gunicorn, and containerize with Docker for consistent releases.