If you want to learn Python or improve your skills, a detailed plan can help you gauge your current status and navigate toward a target goal. This tutorial will help you craft a personal Python learning roadmap so you can track your progress and stay accountable to your goals and timeline:
The steps in this tutorial are useful for Python developers and learners of all experience levels. While you may be eager to start learning, you might want to set aside an hour or two to outline a plan, especially if you already know your learning goals. If you don’t yet have clear goals, consider spreading that reflection over a few shorter sessions across several days to clarify your direction.
Before you start, gather a few practical tools to support building your plan. This might include a notebook, a calendar or planner (digital or physical), a list of projects or goals you want to work toward, and any Python books or online resources you plan to use.
Note: If you learn best with structure and accountability, you can also follow your roadmap inside a cohort-based live course delivered by Real Python experts, with weekly live classes and live Q&A.
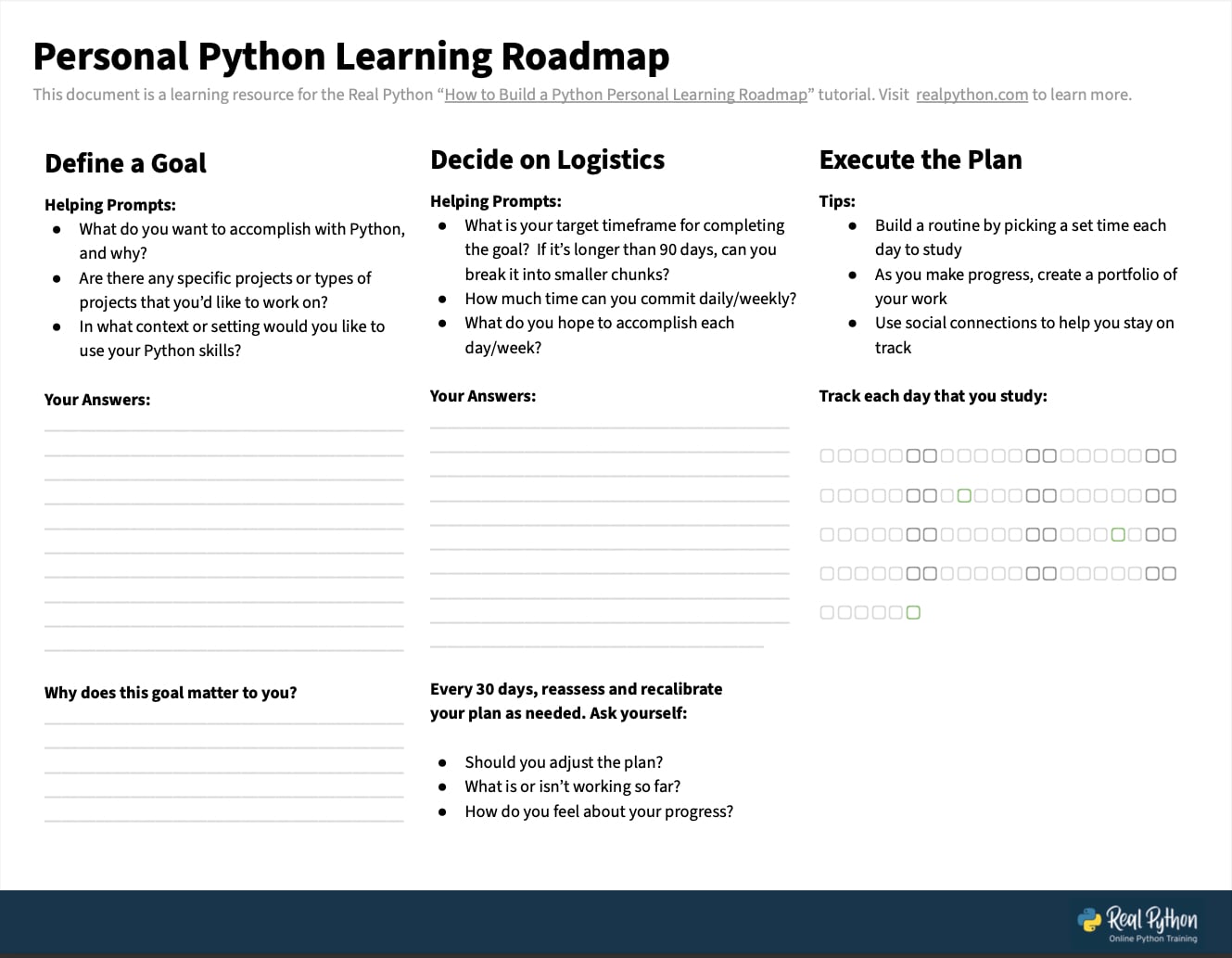
You can download a Personal Python Learning Roadmap worksheet to help you create your plan by clicking the link below:
Get Your Python Learning Roadmap: Click here to download a free, fillable Python learning roadmap PDF to help you set your aims and track your progress.
This tutorial will guide you through the planning process, starting with clarifying what you want to achieve and why. From there, you’ll map out the practical steps that will turn your goals into a realistic, actionable roadmap.
Take the Quiz: Test your knowledge with our interactive “Python Skill Test” quiz. You’ll receive a score upon completion to help you track your learning progress:
Interactive Quiz
Python Skill TestTest your Python knowledge in a skills quiz with basic to advanced questions. Are you a Novice, Intermediate, Proficient, or Expert?
Step 1: Define Your Goals and Motivation
To create an effective learning roadmap, you first need to know what you want to achieve and what your motivation is. For this step, you’ll consider the following reflection prompt:
What do I want to accomplish with Python, and why?
Taking the time to answer this question sets the foundation for every decision you’ll make as you build your roadmap.
Define Your Goals
Start by deciding what you want to accomplish with Python, then write it down. Research shows that this small step can make a meaningful difference. In a study conducted by psychology researcher Dr. Gail Matthews at Dominican University of California, participants who wrote down their goals were significantly more likely to achieve them than those who didn’t.
If you’re not sure yet about your goals, here are some questions for you to consider:
-
Are there specific projects—or types of projects—that you’d like to work on? For example, data analysis, game development, or building a web app.
-
In what context or setting would you like to use your Python skills? For example, at work, in school, or as part of a personal interest or side project.
Remember to write these answers down either in your notebook or on the Personal Python Learning Roadmap worksheet included in this tutorial’s downloads. Having them written down will provide helpful context as you continue formulating your roadmap.
Determine Your Motivation
Once you have a general goal in mind, think about why you want to achieve it. Your motivation plays a key role in whether you’ll stick with your plan over time. As clinical psychology professor Dr. Jennifer Crawford explains:
If we don’t care about why we’re doing [a goal], then it makes it really difficult to stick with that new behavior.
— Dr. Jennifer Crawford
She also encourages goal-setters to ask how their goals connect with something that’s important to them.
This idea is echoed by psychology professor Angela Duckworth in her book Grit, where she emphasizes that a strong sense of purpose helps you persevere when you encounter obstacles that might otherwise derail your progress.
Some possible reasons behind your “why” might include:
- A personal interest or a love of learning
- A desire to start or advance a career in software development
- A goal of earning a computer science degree
- An interest in volunteering your skills—for example, creating a Python application that supports a cause you care about
As you consider your motivation, see if you can dive deeper into the root of your reasons. A deeper look can add even more meaning and staying power to your goals. For example:
- A software development career might allow you to support your family while taking on intellectually fulfilling work
- Earning a computer science degree might help you set a positive example for your family or community
When your goals are anchored in a deeper sense of purpose, you’ll have something to return to when learning feels difficult or progress slows. Take a moment to ask yourself why this goal truly matters to you—and be sure to jot your reasons down so you can revisit them later.
Look at Real-Life Examples
As you’re considering these questions, it might be helpful to see some examples of real people who have set and achieved similar goals. Members of the Real Python community have shared many success stories about setting clear goals and following through on them.
For example, community member Christopher Scogin realized that debugging was a problem for him. He often spent more time fixing issues than writing new code. After committing to work through Real Python’s debugging resources, he significantly reduced the time and effort he spent debugging his programs.
Here’s Christopher describing his experience in his own words:
Now that you’ve defined what you want to achieve and why, it’s time to turn that intention into a concrete plan.
Step 2: Create Your Python Learning Roadmap
Once you’ve defined your goal and motivation, you can focus on the practical details. By the end of this step, you’ll have a written roadmap that outlines how you’ll move forward.
Find Your Starting Point
It might be helpful to determine your initial level of Python expertise. Real Python provides a Python Skill Test quiz to assess your current skills:
Take the Quiz: Test your knowledge with our interactive “Python Skill Test” quiz. You’ll receive a score upon completion to help you track your learning progress:
Interactive Quiz
Python Skill TestTest your Python knowledge in a skills quiz with basic to advanced questions. Are you a Novice, Intermediate, Proficient, or Expert?
Once you complete it, you’ll get answers to these questions:
- What is your current skill level—novice, intermediate, proficient, or expert?
- Which topics do you need to review or learn more about?
- What learning paths and projects are recommended for your level?
Armed with your results, you’ll gain a starting point for your next steps.
Choose Your Learning Resources
Next, choose learning resources to guide your learning. You might start with a Real Python learning path recommended by your skills assessment results, or you can explore other paths that align with your goals. Real Python offers curated learning paths for many topics, including data science and interview preparation. You can also ask for feedback through community resources such as the Real Python community chat or Office Hours.
Tip: If you want a more guided path than self-paced resources, check out the upcoming Real Python Live Courses. You’ll study daily materials on your schedule, then meet for live sessions for feedback and Q&A alongside a small cohort of peers.
Besides Real Python, you could also use the official Python tutorial as a learning path or as supplemental material. Consider other resources, such as Scrimba’s browser-based courses or LearnPython.org’s interactive tutorials.
Hands-on practice through projects and problem-solving exercises is also critical, as practical application builds coding skills. Some Real Python paths include exercise-based courses, but additional resources include:
- Python Projects You Can Build: A collection of step-by-step tutorials
- Python Project: Build a Word Count Command-Line App: An in-depth coding challenge with tutorial videos
- 13 Project Ideas for Intermediate Python Developers: Starting-point suggestions for more challenging projects
You can also look to dedicated practice platforms for exercises and inspiration:
- HackerRank: An online platform that lets you solve short Python problems, connect with employers, and prepare for job interviews
- Practice Python: A list of beginner Python exercises with solutions and discussion
- PYnative: Tutorials, exercises, and quizzes organized by topic, plus an online code editor
These resources can greatly enhance your skill retention and understanding. You don’t have to use these specific suggestions, so feel free to add your own resources to your plan. If you’re using the worksheet that accompanies this tutorial, don’t forget to fill it in with your learning path and resources.
Establish a Timeline
Next, choose a time frame. If you already have a hard deadline, it might already be decided for you. For example, if you’re starting an internship at a set date and want to develop Python skills, that’s an external timeline constraint.
Otherwise, consider a 90-day timeline. A study conducted by psychology researcher Dr. Phillippa Lally’s team found that it takes an average of 66 days to form a new habit, with a variance of up to 254 days. Many businesses and mentors cite 90 days as a healthy range for goal-setting. A 90-day window meshes with quarterly business schedules and provides enough time to build momentum while still being short enough to reassess and adjust as needed.
Note: If you’d rather not invent a timeline from scratch, a cohort-based live course can give you a ready-made schedule. Real Python Live Courses run as an 8-week program, which is a perfect time frame to kickstart your habit building.
If your timeline is longer, consider breaking it into chunks of 90 days or less. For example, a goal like starting a software career without coding experience could take well over 90 days.
Make a Regular Time Commitment
Examine how much time you can set aside weekly, considering commitments like work and family. Be sure to include seasonal and temporary commitments.
Regarding session length, some studies suggest that highly effective students study for three to four hours daily. However, that schedule isn’t feasible for many busy adults with jobs and families.
Entrepreneurial researcher Josh Kaufman suggests that 20 hours—roughly 40 minutes a day for a month—of dedicated practice is sufficient to gain skill competence, even skipping some days. You can break this into two 20-minute daily sessions.
Plan Your Routine
Establish a routine for periodically reviewing your progress. First, determine a weekly goal, like watching one video per day or completing one chapter or tutorial each week.
Also consider how you’ll know when you’ve completed a lesson. Some possible criteria include:
- Passing a lesson quiz
- Making flashcards
- Writing a one-page summary of the material
Take one day a week to reflect on your progress. Review what you’ve learned and what new skills you’ve acquired. Consider taking a weekly quiz, reviewing flashcards, or working on a short project.
Every 30 days, reassess and recalibrate your plan as needed. Ask yourself:
- Should you adjust the plan?
- What is or isn’t working so far?
- How do you feel about your progress?
By now, you should have a written plan for your Python goal. Remember, it’s alright to be flexible and make changes as you put your plan into action.
Step 3: Execute Your Learning Roadmap
Once you’ve written down your plan, it’s time to execute it. This step focuses on building and sustaining your momentum as you follow your roadmap.
Build Consistency and Track Progress
Consistency is one of the keys to success. Earlier, you read about using some kind of planner or calendar. You can use this tool to track each day that you study and follow the plan.
You might even want to keep track of your daily study streaks. Using a digital tool can make streak-tracking easier. Check your phone or other devices to see whether they include built-in habit or streak-tracking features. Here are some other habit-tracking apps to consider:
- Todoist: A to-do list app that allows you to integrate your calendar, email, and other productivity tools
- everyday: A habit tracker that makes it easy to visualize your progress
- Habitify: A productivity toolkit app
- Habitica: A motivational habit and goal tracker that gamifies your goals with in-game rewards and quests
- Habit Hunter: Another gamified habit tracker
If possible, build a routine by picking a set time each day to study. It’s often easier to schedule other commitments around a predictable block of dedicated study time. Let family members and others know that you need some uninterrupted time.
Create Visual Evidence of Progress
In addition to streaks, there are other ways to establish a visible record of your progress. This visibility can help keep you motivated and accountable. Going too long without seeing any evidence of progress can sap motivation, while visible progress can spur you back into action.
If you’re using Real Python learning paths and resources, remember to update their status as you work through them. When you begin a course or resource, you can bookmark it, and Real Python will automatically mark courses you’ve started engaging with as “in-progress”. This makes it easier to see what you’re working on and pick up where you left off. Be sure to mark each resource as completed when you’re done.
Studying is important, but applying your skills to create something is vital. As you make progress, create a portfolio of your work. Consider making a dedicated folder or workspace on your computer or in an online coding environment. If you store all your Python projects and practice there, you can quickly see your accomplishments.
You can also create a website or online portfolio to share your best work with potential employers or other audiences. Alternatively, you can create a GitHub profile and publish your work there.
Enlist Community for Accountability
If you prefer, you can also use social connections to help you stay on track. The same study by Dr. Matthews referenced earlier shows that participants who sent weekly progress reports to a friend and made public commitments to their goals had significantly higher success rates.
If you’d like to add social accountability, but don’t know anyone personally whom you’d feel comfortable asking for support, there are other options. You can share your progress on social media: hashtags like #100daysofcode, #devcommunity, and #buildinpublic can bring visibility and support to your journey.
The Real Python community can also be helpful, especially the Slack #hangout channel, where you can share your week’s achievements every Friday.
You can also check to see if there are any local or virtual Python learning meetups or group challenges you can join. Having a dedicated cohort of other learners is a great way to establish a network for future project and job opportunities.
Tip: If you want built-in accountability, then check out Real Python’s live cohorts. In those courses, you’re part of a small cohort of dedicated peers. Everyone’s there to learn Python on a regular schedule, which will keep you engaged. Additionally, you’re already building your professional network from the get-go.
Pace Yourself
Avoiding burnout and maximizing your brain’s learning capability is critical. One approach is to opt for shorter study sessions, rather than long, marathon sessions. Consider the Pomodoro Technique, in which you set a timer for 25 minutes and focus on one task for that time frame. You then take a five-minute break when the timer goes off.
Another technique is to space out your study sessions. Rather than cramming all at once, add some time between your study sessions to improve your long-term retention of the material. As suggested earlier, try splitting your daily studying into two sessions, perhaps one in the morning and another at night.
Next Steps
Now you know how to identify your Python learning goals and craft a plan. Your next step is to get started! Here’s a quick recap of where to go from here.
As suggested earlier, taking the Python Skill Test is a good first step:
Take the Quiz: Test your knowledge with our interactive “Python Skill Test” quiz. You’ll receive a score upon completion to help you track your learning progress:
Interactive Quiz
Python Skill TestTest your Python knowledge in a skills quiz with basic to advanced questions. Are you a Novice, Intermediate, Proficient, or Expert?
Next, choose one or two learning paths. In addition to the recommended paths in your assessment results, consider exploring these other resources:
- Python Learning Paths on Real Python
- Python Books by Real Python
- The other resources listed in Step 2
And remember, you can also join Real Python’s community and Office Hours to get extra feedback from like-minded peers on your next steps.
Get Your Python Learning Roadmap: Click here to download a free, fillable Python learning roadmap PDF to help you set your aims and track your progress.
Frequently Asked Questions
As you create and then execute your roadmap, you might have some questions. Here are some common questions that could pop up on your journey. Click the Show/Hide toggle beside each question to reveal the answer.
If you need to make adjustments, revisit the previous steps. If your plan or learning resources no longer fits with your goal, circle back to Step 1 and the learning resources section of Step 2. If your goal and overall plan are still aligned but you’re having logistical problems, revisit all of Step 2.
Congratulations if you’re able to finish your roadmap early! In this case, consider adding some extra “down the road” goals during the planning stages. You can move on to these goals if you hit your target early.
If you didn’t finish before the allotted time, that’s okay! You can start another time cycle as needed. Aim for 30-day periods. If you’re almost done with the roadmap, another 30 days might suffice. Otherwise, try another 60 or 90 days, and you can reassess after that.
If you seriously fall behind, you might need to add some more time to your original target time. Otherwise, there are some options you can try. To help you stay on track, have some daily minor “wins” that you can do even if you’re pressed for time, like flashcards you can squeeze in during odd minutes in the day.
During the planning stage, plan for slightly less than you think you can accomplish in your allotted time frame. This way, you have some wiggle room if you get off track.
If you learn best with a clear schedule and regular check-ins, then a cohort-based approach can be a good fit. In addition to self-paced learning paths and community support, Real Python also offers cohort-based live courses with weekly live sessions and live Q&A.
The answer to this question depends on your current skill level, compared to your desired level of proficiency. If you’re starting with no Python experience but want to get a job, it could take around four hours of daily study for four months. That’s approximately 480 hours.
It can take years to reach a level of proficiency that would be widely considered expert-level.
If you get stuck often or you want quicker feedback, then add more support to your plan. You can ask questions in the Real Python community and during Office Hours. You can also join a cohort-based live course for guided weekly sessions and live Q&A with an expert instructor.
Take the Quiz: Test your knowledge with our interactive “Python Skill Test” quiz. You’ll receive a score upon completion to help you track your learning progress:
Interactive Quiz
Python Skill TestTest your Python knowledge in a skills quiz with basic to advanced questions. Are you a Novice, Intermediate, Proficient, or Expert?