Python 3.14 was released on October 7, 2025. While many of its biggest changes happen under the hood, there are practical improvements you’ll notice right away. This version sharpens the language’s tools, boosts ergonomics, and opens doors to new capabilities without forcing you to rewrite everything.
In this tutorial, you’ll explore features like:
- A smarter, more colorful REPL experience
- Error messages that guide you toward fixes
- Safer hooks for live debugging
- Template strings (t-strings) for controlled interpolation
- Deferred annotation evaluation to simplify typing
- New concurrency options like subinterpreters and a free-threaded build
If you want to try out the examples, make sure you run Python 3.14 or a compatible preview release.
Note: On Unix systems, when you create a new virtual environment with the new Python 3.14, you’ll spot a quirky alias:
(venv) $ 𝜋thon
Python 3.14.0 (main, Oct 7 2025, 17:32:06) [GCC 14.2.0] on linux
Type "help", "copyright", "credits" or "license" for more information.
>>>
This feature is exclusive to the 3.14 release as a tribute to the mathematical constant π (pi), whose rounded value, 3.14, is familiar to most people.
As you read on, you’ll find detailed examples and explanations for each feature. Along the way, you’ll get tips on how they can streamline your coding today and prepare you for what’s coming next.
Get Your Code: Click here to download the free sample code that you’ll use to learn about the new features in Python 3.14.
Take the Quiz: Test your knowledge with our interactive “Python 3.14: Cool New Features for You to Try” quiz. You’ll receive a score upon completion to help you track your learning progress:
Interactive Quiz
Python 3.14: Cool New Features for You to TryIn this quiz, you'll test your understanding of the new features introduced in Python 3.14. By working through this quiz, you'll review the key updates and improvements in this version of Python.
Developer Experience Improvements
Python 3.14 continues the trend of refining the language’s ergonomics. This release enhances the built-in interactive shell with live syntax highlighting and smarter autocompletion. It also improves syntax and runtime error messages, making them clearer and more actionable. While these upgrades don’t change the language itself, they boost your productivity as you write, test, and debug code.
Even Friendlier Python REPL
Python’s interactive interpreter, also known as the REPL, has always been the quickest way to try out a snippet of code, debug an issue, or explore a third-party library. It can even serve as a handy calculator or a bare-bones data analysis tool. Although your mileage may vary, you typically start the REPL by running the python command in your terminal without passing any arguments:
$ python
Python 3.14.0 (main, Oct 7 2025, 17:32:06) [GCC 14.2.0] on linux
Type "help", "copyright", "credits" or "license" for more information.
>>>
The humble prompt, which consists of three chevrons (>>>), invites you to type a Python statement or an expression for immediate evaluation. As soon as you press Enter, you’ll instantly see the computed result without having to create any source files or configure a project workspace. After each result, the familiar prompt returns, ready to accept your next command:
>>> 2 + 2
4
>>>
For years, the stock Python REPL remained intentionally minimal. It was fast and reliable, but lacked the polish of alternative shells built by the community, like IPython, ptpython, or bpython.
That started to change in Python 3.13, which adopted a modern REPL based on PyREPL borrowed from the PyPy project. This upgrade introduced multiline editing, smarter history browsing, and improved Tab completion, while keeping the simplicity of the classic REPL.
Python 3.14 takes the interactive shell experience to the next level, introducing two new features:
- Syntax highlighting: Real-time syntax highlighting with configurable color themes
- Code completion: Autocompletion of module names inside
importstatements
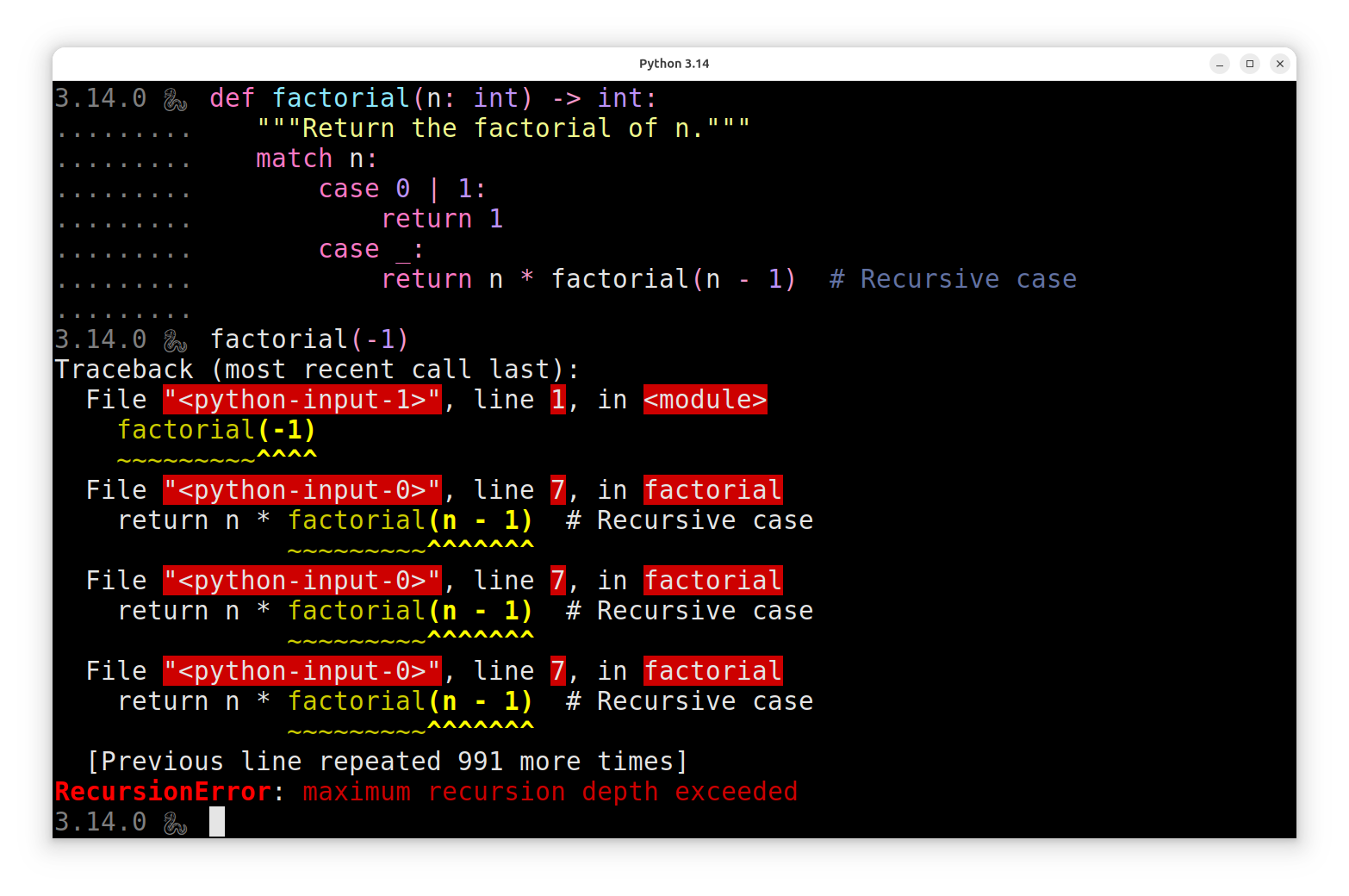
Together, these improvements make the built-in REPL feel closer to a full-fledged code editor while keeping it lightweight and always available. The Python REPL now highlights code as you type. Keywords, strings, comments, numbers, and operators each get their own color, using ANSI escape codes similar to those that already color prompts and tracebacks in Python 3.13:
Notice how the colors shift as you type, once the interactive shell has enough context to parse your input. In particular, tokens such as the underscore (_) are recognized as soft keywords only in the context of pattern matching, and Python highlights them in a distinct color to set them apart. This colorful output also shows up in the Python debugger (pdb) when you set a breakpoint() on a given line of code, for example.
Additionally, a few of the standard-library modules can now take advantage of this new syntax-coloring capability of the Python interpreter:
The argparse module displays a colorful help message, the calendar module highlights the current day, the json module pretty-prints and colorizes JSON documents. Finally, the unittest module provides a colorful output for failed assertions to make reading and diagnosing them easier.
If you’re not a fan of the default colors in Python 3.14, then you can customize them using experimental theming support. To make your tweaks persistent, you may want to specify a custom Python startup script like the one below:
~/.pythonrc.py
# Set a custom color theme in Python 3.14
try:
from _colorize import ANSIColors, default_theme, set_theme
except ImportError:
pass
else:
custom_theme = default_theme.copy_with(
syntax=default_theme.syntax.copy_with(
prompt=ANSIColors.GREY,
builtin="\x1b[38;2;189;147;249m",
comment="\x1b[38;2;98;114;164m",
definition="\x1b[38;2;139;233;253m",
keyword="\x1b[38;2;255;121;198m",
keyword_constant="\x1b[38;2;255;121;198m",
soft_keyword="\x1b[38;2;255;121;198m",
number="\x1b[38;2;189;147;249m",
op="\x1b[38;2;249;152;204m",
string="\x1b[38;2;241;250;140m",
),
traceback=default_theme.traceback.copy_with(
error_highlight=ANSIColors.BOLD_YELLOW,
error_range=ANSIColors.YELLOW,
filename=ANSIColors.BACKGROUND_RED,
frame=ANSIColors.BACKGROUND_RED,
line_no=ANSIColors.BACKGROUND_RED,
message=ANSIColors.RED,
type=ANSIColors.BOLD_RED,
)
)
set_theme(custom_theme)
# Set a custom shell prompt
import platform
import sys
version = platform.python_version()
sys.ps1 = f"{version} \N{SNAKE} "
sys.ps2 = "." * len(sys.ps1)
This script runs each time you start a new interactive Python REPL session. In this case, it checks whether the new _colorize module introduced in Python 3.14 is available. If so, it uses the module to override the default colors for the Python syntax and tracebacks, mimicking the popular Dracula theme. As a bonus, it also customizes the default prompt to display the interpreter’s version.
When you run the Python interpreter now, this is what the result will look like:
You’ve tweaked the colors of the Python syntax and tracebacks, while keeping the default colors for the standard-library modules mentioned earlier. Keep in mind that this API is still experimental, so future Python releases may change it. Treat it as a convenient but temporary feature!
Note: If you’d like to disable colors entirely, then set one of the following environment variables in your shell:
NO_COLOR=1PYTHON_COLORS=0
Either variable turns off color output while preserving other REPL features, including autocompletion. To bring back the classic Python REPL, set the PYTHON_BASIC_REPL=1 variable instead.
Previously, the REPL could automatically complete variables and attributes, but import statements were left to memory. Python 3.14 now extends Tab completion to recognize the context of an import and from … import clauses, suggesting module and package names drawn from your current import path:
Type import and press Tab twice to display a list of all available top-level modules and packages. If the list doesn’t fit on your screen, then keep pressing Tab to cycle through the paginated results.
To narrow down your options, start typing a partial name like dat. The list will now only include matches such as dataclasses and datetime. If you type data, then there’s only one possible match, so Python will autocomplete it for you immediately. Otherwise, confirm the selection with another press of Tab.
When you type import followed by an ambiguous prefix, and then hit Tab, you’ll see a warning that the match isn’t unique. Press Tab again to show the full list and choose the correct module.
To explore internal or non-public modules, type import _ and press Tab to reveal names starting with an underscore.
The same logic applies to a from … import … statement. After from, pressing Tab lists candidate modules or subpackages. After import, it lists submodules. For performance reasons, though, the REPL doesn’t introspect a module’s contents to suggest object names such as functions or classes.
This enhancement is particularly handy for exploratory programming or learning new libraries, letting you discover available modules without leaving the interpreter or consulting documentation.
Note: For a hands-on tour of the new Python REPL enhancements, check out Python 3.14: REPL Autocompletion and Highlighting.
More Helpful Error Messages
Python 3.14 continues the ongoing work to make error messages more helpful, especially for beginners. It builds on the parsing expression grammar introduced in Python 3.9 and the steady improvements made in subsequent releases:
- Python 3.10: Better Error Messages
- Python 3.11: Even Better Error Messages
- Python 3.12: Ever Better Error Messages
- Python 3.13: Better Error Messages
This Python release sharpens many of the messages you see when your code doesn’t work as expected, covering both syntax errors and runtime exceptions. The result is clearer error messages that make debugging more efficient by helping you find and fix bugs faster.
Instead of simply flagging that something went wrong, Python now pinpoints the root cause and often hints at the remedy, addressing the kinds of mistakes newcomers and veterans alike make most often. Generic “invalid syntax” messages are now more specific and descriptive.
For example, when you make a typo in a keyword, Python 3.14 can often guess what you meant and suggest the correct spelling:
Python 3.14
>>> forr i in range(5):
File "<python-input-0>", line 1
forr i in range(5):
^^^^
SyntaxError: invalid syntax. Did you mean 'for'?
By contrast, earlier versions of the interpreter not only fail to identify the problem but also mislead you by drawing attention to the variable rather than the mistyped keyword:
Python 3.13
>>> forr i in range(5):
File "<python-input-0>", line 1
forr i in range(5):
^
SyntaxError: invalid syntax
Python 3.14 goes further, recognizing and explaining a wide range of common mistakes, such as unterminated string literals, incompatible string literal prefixes, and more:
Python 3.14
>>> message = "She said "Hello" to everyone"
File "<python-input-0>", line 1
message = "She said "Hello" to everyone"
^^^^^
SyntaxError: invalid syntax. Is this intended to be part of the string?
>>> text = fb"Binary {text}"
File "<python-input-1>", line 1
text = fb"Binary {text}"
^^
SyntaxError: 'b' and 'f' prefixes are incompatible
>>> 1 if True else pass
File "<python-input-2>", line 1
1 if True else pass
^^^^
SyntaxError: expected expression after 'else', but statement is given
>>> if x > 0:
... print("positive")
... else:
... print("not positive")
... elif x == 0:
... print("zero")
...
File "<python-input-5>", line 5
elif x == 0:
^^^^
SyntaxError: 'elif' block follows an 'else' block
Beyond the syntax-related improvements described above, several of Python’s built-in exceptions have also been refined. With clearer messages and more informative context, they help you quickly troubleshoot and address issues occurring at runtime:
Python 3.14
>>> import math
>>> math.sqrt(-1)
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<python-input-1>", line 1, in <module>
math.sqrt(-1)
~~~~~~~~~^^^^
ValueError: expected a nonnegative input, got -1.0
>>> left, right = ["apple", "banana", "orange"]
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<python-input-2>", line 1, in <module>
left, right = ["apple", "banana", "orange"]
^^^^^^^^^^^
ValueError: too many values to unpack (expected 2, got 3)
>>> points = {[0, 0]: "origin"}
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<python-input-3>", line 1, in <module>
points = {[0, 0]: "origin"}
^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
TypeError: cannot use 'list' as a dict key (unhashable type: 'list')
As you upgrade to Python 3.14 and encounter these kinds of exceptions in practice, you’ll spend less time deciphering cryptic error messages and more time writing correct, maintainable code.
Note: For a deeper look at these enhanced error messages, see Python 3.14: Better Syntax Error Messages.
Safer Live Process Debugging
Python 3.14 adopts PEP 768, which standardizes a safe and stable interface for connecting external debuggers to the CPython interpreter. Until now, tools like pdb, IDEs, and system-level debuggers like gdb often had to rely on private hooks or internal knowledge of CPython’s implementation details. This approach worked but was fragile. Even small internal changes could break integrations, leading to crashes or incorrect debugging behavior.
The safe external debugger interface builds on a low-level C API exposed by CPython, but comes with a user-facing option you can try today:
$ python3.14 -m pdb -p <PID>
The -p option tells pdb to connect to an already running Python interpreter given its process identifier (PID). Once attached, you can inspect variables, set breakpoints, and step through code as if you had started the process under pdb from the beginning.
The debugger hooks into the main thread of a live process and lets you run snippets of arbitrary Python code within its context. This trick is powered by a new function, sys.remote_exec(), which debuggers call behind the scenes to safely evaluate code inside the target interpreter.
Suppose you’re running a minimal web server that responds to HTTP requests with your browser’s user agent:
web_server.py
1import os
2import sys
3from http.server import BaseHTTPRequestHandler, HTTPServer
4
5HOSTNAME = "localhost"
6PORT = 8000
7
8class Handler(BaseHTTPRequestHandler):
9 def do_GET(self):
10 user_agent = self.headers.get("User-Agent")
11 self.send_response(200)
12 self.end_headers()
13 self.wfile.write(f"Hello, {user_agent}".encode())
14
15def main():
16 print(f"Starting the server on: http://{HOSTNAME}:{PORT}")
17 print("Run this command as a superuser to attach the debugger:")
18 print(f"{sys.executable} -m pdb -p {os.getpid()}")
19 HTTPServer((HOSTNAME, PORT), Handler).serve_forever()
20
21if __name__ == "__main__":
22 main()
Start your server in one terminal window using the following command:
$ python3.14 web_server.py
Starting the server on: http://localhost:8000
Run this command as a superuser to attach the debugger:
/home/realpython/.pyenv/versions/3.14.0/bin/python -m pdb -p 70262
The output shows the server URL and the command to attach the debugger to your Python process, identified by its unique PID.
Now, from another terminal, become the superuser—for example, using the sudo -s command—and paste the command exactly as shown. Alternatively, you can qualify the command with sudo instead of switching users:
$ sudo /home/realpython/.pyenv/versions/3.14.0/bin/python -m pdb -p 70262
You need elevated privileges because the debugger gains access to another process’s memory.
Once inside, place a breakpoint at line 11, just after reading the user agent, and then let the server continue executing:
# /home/realpython/.pyenv/versions/3.14.0/bin/python -m pdb -p 70262
> /home/realpython/.pyenv/versions/3.14.0/lib/python3.14/selectors.py(398)select()
-> fd_event_list = self._selector.poll(timeout)
(Pdb) break web_server:11
Breakpoint 1 at /home/realpython/tutorials/python-314/web_server.py:11
(Pdb) continue
The debugger will stop again when it encounters a breakpoint. So, you need to open your browser now and visit the page at http://localhost:8000 to send a request. Alternatively, you can use a command-line tool like cURL or similar.
Next, go back to your debugger. You’ll be dropped back into the interactive prompt, where you can print (p) and even overwrite the server’s local variables:
> /home/realpython/tutorials/python-314/web_server.py(11)do_GET()
-> self.send_response(200)
(Pdb) p user_agent
'Mozilla/5.0 (X11; Linux x86_64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (...)'
(Pdb) user_agent = "It's magic!"
(Pdb) continue
> /home/realpython/tutorials/python-314/web_server.p(11)do_GET()
-> self.send_response(200)
(Pdb)
When you issue the continue command in the debugger, the server resumes, responding to the client with the new user agent value.
To use this new feature, both the target process and the debugger must run on Python 3.14 or newer. And, while it’s convenient for development, you may not want external debuggers attaching in production. The safe way to disable it is at build time. You can compile CPython with the --without-remote-debug option, which removes the PEP 768 interface entirely so that no external debugger can connect.
If you’re writing Python code, you don’t need to change anything to take advantage of PEP 768. It’s an under-the-hood improvement meant to make the ecosystem healthier. But if you develop tooling around Python, then you now have a dedicated hook into the interpreter instead of reverse-engineering its guts.
New Python Syntax
If you like keeping your code concise and expressive, this release has a few surprises in store. Template strings (t-strings) add a safer way to handle string interpolation, multiple exceptions can be handled without unnecessary parentheses, and finally blocks now follow stricter rules that reduce ambiguity. These syntax tweaks may seem small, but they’ll help you write cleaner and more predictable code.
Template Strings (T-Strings)
Inspired by JavaScript’s tagged template literals, Python’s new template strings (nicknamed t-strings), are likely the most noticeable addition in the 3.14 release. Syntactically, t-strings resemble f-strings very closely, sharing the same placeholder syntax, optional format specifiers, and conversion flags. At first glance, the only visible difference is the prefix since template string literals begin with t or T.
However, unlike f-strings, t-strings evaluate to a new string.templatelib.Template object instead of directly producing a plain str:
Python 3.14
>>> f"This is a formatted string literal (f-string)"
'This is a formatted string literal (f-string)'
>>> t"This is a template string literal (t-string)"
Template(
strings=('This is a template string literal (t-string)',),
interpolations=()
)
The two literal forms look almost identical, making it easy to mistake one for the other, especially when you expect an f-string but accidentally type t instead of f, or the other way around. This subtle difference can lead to surprising bugs if you’re not careful!
Another surprising fact is a bit of an unfortunate choice of names. After all, Python has already shipped with a Template class before, although located in a different package, despite serving a somewhat similar purpose:
| Class | Purpose |
|---|---|
string.Template |
Simple variable substitution using the $variable syntax, introduced in Python 2.4 |
string.templatelib.Template |
Custom string processing logic with safety in mind, introduced in Python 3.14 |
The primary motivation for introducing t-strings and the new Template class was the desire to keep the convenience and readability of f-strings while making them safer. Ultimately, both string literal types can execute arbitrary code inside their placeholder fields. For example, the snippet below reads user input to populate a database query expressed as a formatted string literal:
>>> def find_users_query(name: str) -> str:
... """Return a SQL query to find users by name."""
... return f"SELECT * FROM users WHERE name = '{name}'"
...
>>> find_users_query("alice")
"SELECT * FROM users WHERE name = 'alice'"
>>> find_users_query(input("Enter the user name: "))
Enter the user name: ' OR '1'='1
"SELECT * FROM users WHERE name = '' OR '1'='1'"
While this is a powerful feature, it can introduce serious security vulnerabilities if misused. In this case, interpolating raw user input directly into a query leaves the door open to SQL injection. An attacker can craft malicious input to alter the query’s intended logic, as the highlighted line demonstrates. To mitigate this risk, you should use prepared statements or sanitize user input instead of directly formatting it into the SQL string.
This is where t-strings come into the picture. Unlike f-strings, t-strings intercept the values before they’re merged into the template, adding an extra layer of security. They allow you to validate or sanitize the input, so you can enforce types, escape or reject dangerous characters, or convert values into safe parameter placeholders that the database driver can handle.
By changing the definition of your find_users_query() function so that it returns a string template instead of a plain string, you can delay the substitution of user-supplied values:
Python 3.14
>>> from string.templatelib import Template
>>> def find_users_query(name: str) -> Template:
... """Return a SQL query to find users by name."""
... return t"SELECT * FROM users WHERE name = '{name}'"
...
>>> find_users_query("' OR '1'='1")
Template(
strings=("SELECT * FROM users WHERE name = '", "'"),
interpolations=(
Interpolation("' OR '1'='1", 'name', None, ''),
)
)
Notice that the resulting template object retains each pair of curly braces ({}) that appears in the t-string literal as a string.templatelib.Interpolation instance. This object contains both the evaluated value of an arbitrary data type, like "alice" or 42, as well as the corresponding Python expression—for example, "name" or "input('Your age: ')"—decompiled from the placeholder field into a string representation.
Note: A t-string literal evaluates its placeholder expressions eagerly, just like an f-string literal does. This means that all placeholders must be known upfront when the template string literal is defined. Wrapping the t-string in a function defers their evaluation.
Okay, but how exactly do you turn such a template object into a SQL query string? As of Python 3.14, you must write your own template processor or find one in a third-party library. The current release only specifies the syntax for t-string literals, along with the helper string.templatelib module and the two classes, Template and Interpolation.
There are plans to include template string consumers in the standard library in future releases. The most notable one is documented in PEP 787, which proposes extending the subprocess and shlex modules to natively support t-strings.
You can implement a t-string processor as a function that takes a template object as an argument, applies some transformations, and produces either a safe str or another structured object. For example, it could be an abstract representation of an HTML element or a parameterized SQL statement.
The most straightforward way to convert a template object into a string is to interleave its fixed text segments with the interpolation values using zip(), str.join(), and a generator expression:
Python 3.14
>>> def render(template: Template) -> str:
... return "".join(
... f"{text}{value}"
... for text, value in zip(template.strings, template.values)
... )
...
>>> render(find_users_query("' OR '1'='1"))
"SELECT * FROM users WHERE name = '' OR '1'='1"
This code is essentially equivalent to your earlier f-string example, which suffers from the same shortcomings as before. To leverage the true power of t-strings, you can take advantage of the fact that Template is iterable:
Python 3.14
>>> def safer_render(template: Template) -> str:
... items = []
... for item in template:
... if isinstance(item, str):
... items.append(item)
... else:
... sanitized = str(item.value).replace("'", "''")
... items.append(sanitized)
... return "".join(items)
...
>>> safer_render(find_users_query("' OR '1'='1"))
"SELECT * FROM users WHERE name = ''' OR ''1''=''1'"
Under the hood, Template is a sequence of interleaved strings and interpolation values that you can loop over. This implementation uses a pretty straightforward sanitization technique, which escapes each single quote (') by doubling it (''). As a result, your SQL injection attempts fail because the injected text remains inside the quoted string literal, treated as data rather than executable SQL.
Still, this is only a rudimentary form of protection. For real SQL safety, you should rely on parameterized queries of your database driver instead of hand-rolled string fixes. Moreover, you don’t always have to turn a t-string into a plain string. Here’s a more complete and sophisticated example:
Python 3.14
>>> from dataclasses import dataclass
>>> from string.templatelib import Interpolation, Template, convert
>>> from typing import Any
>>> @dataclass(frozen=True)
... class SQLQuery:
... statement: str
... params: list[Any]
...
... def __init__(self, template: Template) -> None:
... items, params = [], []
... for item in template:
... match item:
... case str():
... items.append(item)
... case Interpolation(value, _, conversion, format_spec):
... converted = convert(value, conversion)
... if format_spec:
... converted = format(converted, format_spec)
... params.append(converted)
... items.append("?")
... super().__setattr__("statement", "".join(items))
... super().__setattr__("params", params)
...
You define an immutable data class, which represents a parameterized SQL query. Its constructor takes a string template as an argument. It then iterates over that template with a for loop and uses pattern matching to process the fixed string values and the interpolation values differently. Notice also how you call convert() and format() to manually apply the formatting, unlike f-strings that do this behind the scenes.
Here’s how you can incorporate your new data class into the query-building function:
Python 3.14
>>> def find_users(name: str) -> SQLQuery:
... """Return a SQL query to find users by name."""
... return SQLQuery(t"SELECT * FROM users WHERE name = {name}")
...
>>> find_users("' OR '1'='1")
SQLQuery(
statement='SELECT * FROM users WHERE name = ?',
params=["' OR '1'='1"]
)
When you run this SQLQuery through a Python Database API, the corresponding driver will try to bind the parameters to the placeholders for you. Because the malicious string is treated strictly as a literal value, not executable SQL, the attempted injection is safely neutralized.
Note: Check out Python 3.14: Template Strings to explore t-strings in more detail.
Exceptions Without Parentheses
Python 3.14 adopts PEP 758, a small but welcome tweak to exception-handling syntax. Until now, when catching multiple exceptions, you had to wrap them in parentheses:
try:
int("one")
except (ValueError, TypeError):
print("Something went wrong")
Otherwise, you’d end up with a syntax error:
>>> try:
... int("one")
... except ValueError, TypeError:
... print("Something went wrong")
...
File "<python-input-0>", line 3
except ValueError, TypeError:
^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
SyntaxError: multiple exception types must be parenthesized
Starting in Python 3.14, the parentheses become optional if you’re not using the as keyword. This means you can now write the following:
Python 3.14
>>> try:
... int("one")
... except ValueError, TypeError:
... print("Something went wrong")
...
Something went wrong
The new syntax also applies to except* clauses, which are used to catch exception groups. In practice, this change makes exception handling more consistent with other comma-separated constructs in Python, such as tuple literals, where parentheses aren’t strictly required. It also reduces visual clutter when the list of exceptions grows long.
If you want to bind the caught exception to a variable with as, then parentheses remain mandatory for clarity:
Python 3.14
try:
int("one")
except (ValueError, TypeError) as e:
print("Error:", e)
This avoids ambiguity about what exactly is being assigned to the variable. Aside from the syntactic sugar, nothing changes in behavior. The interpreter still handles exceptions the same way.
While minor, this adjustment streamlines a very common pattern in Python programs, making code a little more readable without breaking backward compatibility. If you’ve been writing except (ErrorA, ErrorB), you can keep doing so, but now you also have the option to drop the parentheses when they feel unnecessary.
Note: For a deeper explanation of how this change came about, check out the Python News for April 2025.
Warnings in try…finally Blocks
Python’s try…finally blocks are designed to guarantee that cleanup code runs no matter how the try block exits—whether it finishes normally, raises an exception, or hits a return statement. However, using certain control flow structures inside finally has long been considered problematic.
If you return, break, or continue from a finally block, then you can silently override an active exception or skip important cleanup, leading to confusing and unintended behavior. Consider this contrived example:
Python ≤ 3.13
>>> def risky_operation():
... try:
... raise ValueError("Something went wrong!")
... finally:
... return "Suppressed"
...
>>> risky_operation()
'Suppressed'
In Python 3.13 and earlier, this function would swallow the ValueError entirely and return the string "Suppressed". The caller would never see the exception, which makes debugging extremely difficult. A similar effect occurs when you use break or continue inside a finally block. All of these keywords can override control flow in ways that hide the original reason the block was triggered.
For years, this quirk has been a known “footgun” in the language. At one point, Python’s core team considered banning it outright. Instead, PEP 765 struck a compromise. Starting in Python 3.14, such usage is still legal for backward compatibility, but the interpreter now issues a SyntaxWarning to make the risk explicit:
Python 3.14
>>> def risky_operation():
... try:
... raise ValueError("Something went wrong!")
... finally:
... return "Suppressed"
...
<python-input-0>:5: SyntaxWarning: 'return' in a 'finally' block
>>> risky_operation()
'Suppressed'
This warning is your hint that the control flow inside the finally block could be dangerous. The code still runs as before, but you now get a clear heads-up that something odd is happening.
The same applies to break and continue:
Python 3.14
>>> while True:
... try:
... raise RuntimeError
... finally:
... break
...
<python-input-2>:5: SyntaxWarning: 'break' in a 'finally' block
You can treat these warnings as an opportunity to revisit your design. Usually, the fix is simple: move the control flow statement outside of the finally, or restructure the logic so that the finally block only does cleanup, not flow control. For example, if you need to return a value, compute it in the try block and let the finally run afterward:
>>> def safer_function():
... try:
... result = "Suppressed"
... raise ValueError("Something went wrong!")
... finally:
... print("Cleaning up...")
... return result
...
>>> safer_function()
Cleaning up...
Traceback (most recent call last):
...
ValueError: Something went wrong!
Here, the cleanup still happens, but the exception is no longer lost.
Because this change is limited to a SyntaxWarning, existing codebases won’t suddenly fail when running under Python 3.14. But with these warnings, you’ll get immediate insight into any questionable patterns. This gives you time to audit and adjust your code before future releases potentially escalate the warning into an error.
In short, Python 3.14 shines a light on a long-standing corner case of the language. By warning you about the return, break, and continue statements in finally blocks, it nudges you toward safer, more predictable patterns, without cutting off existing code overnight.
Type Checking Revolution
This section highlights the biggest advances in Python’s type system in 3.14, building on years of incremental refinements. To put these changes in perspective, you’ll take a brief tour of the history of typing in Python. If you’re already familiar with that background, then feel free to skip ahead to the discussion of deferred evaluation of annotations in Python 3.14.
A Quick Tour of Typing History
Among all the enhancements in Python 3.14, the most disruptive one is the brand-new way the interpreter evaluates annotations. If you rely on type hints for static type checking or use libraries that process annotations dynamically at runtime, then this change will make your code simpler, less error-prone, and potentially even faster. It represents the biggest single leap for Python’s type-hinting ecosystem in years.
In the lead-up to this release, Python had already been steadily improving its type system. Here are just a handful of examples from earlier versions, which include new modules and refinements to the Python syntax:
- Python 3.7:
from __future__ import annotations - Python 3.8:
Final,Literal,TypedDict,Protocol - Python 3.9:
Annotated, generic collections - Python 3.10: type aliases, guards, parameters, unions
- Python 3.11:
Self, variadic generics - Python 3.12:
@override, type variable syntax - Python 3.13:
ReadOnly,TypeIs, type defaults
One of the most highly anticipated updates to Python’s type system is the introduction of lazy evaluation of annotations, which aims to resolve long-standing issues in type-hinting scenarios. Yet, implementing this new feature correctly has proven more challenging than expected.
Traditionally, Python evaluated type annotations at definition time, much the same way it handles default argument values in function signatures. However, such an eager evaluation sometimes caused problems, ranging from reduced startup performance to reference cycles to circular import errors.
Consider the following example, where you want to define a linked list data structure consisting of a chain of nodes:
linked_list.py
1from dataclasses import dataclass
2from typing import Any, Optional
3
4@dataclass
5class LinkedList:
6 head: Node
7
8@dataclass
9class Node:
10 value: Any
11 next: Optional[Node] = None
Running this code in Python 3.13 or earlier raises a NameError because the interpreter can’t recognize Node, which you used on line 6 to annotate the .head attribute:
$ python3.13 linked_list.py
Traceback (most recent call last):
...
head: Node
^^^^
NameError: name 'Node' is not defined. Did you mean: 'None'?
At this point, the Node class hasn’t been defined yet. Reordering your class definitions can sometimes help, but in this case, you’d only shift the problem from one place to another. Notice that Node also refers to itself through the .next attribute, resulting in a similar situation, since the self-referencing class hasn’t been completely defined.
To circumvent this, you need a way to stop Python from immediately evaluating annotations as soon as it encounters them.
The concept of postponed evaluation of annotations first appeared in PEP 563. This feature became available in Python 3.7 as an optional __future__ import, which would override the interpreter’s default behavior on a per-module basis:
Python 3.7-3.13
>>> variable1: print("This code runs immediately.")
This code runs immediately.
>>> from __future__ import annotations
>>> variable2: print("This code becomes a string.")
>>> __annotations__
{
'variable1': None,
'variable2': "print('This code becomes a string.')"
}
By default, previous Python versions would run the annotation’s code instantly. Since calling print() has a visible side effect in the form of updating the standard output stream, you can see the message being displayed on your screen right away. This shows that Python executes annotations behind the scenes, even though it’s not particularly concerned with their computed values.
Note: Although annotations often describe data types, they can just as easily be any valid Python expressions, provided that they comply with Python syntax. Now you know why!
By contrast, once you enable the mentioned future directive, the subsequent code is treated differently. Python no longer evaluates annotations, leaving this job to you. Instead, with a bit of low-level magic, it preserves your annotations as plain strings, as if you had manually wrapped each one in quotes to form string literals.
Inspecting the special __annotations__ dictionary reveals two module-level variable annotations:
variable1is annotated withNonereturned byprint().variable2is annotated with a stringified Python expression.
Whether annotations are strings or other Python objects makes no difference to type checkers like mypy or ty, which perform static code analysis. However, libraries that inspect annotations at runtime—say, for dependency injection or data validation—may need to resolve those stringified annotations themselves to recover the original values.
Storing annotations as strings prevents undefined reference errors and avoids the extra cost of evaluating heavy expressions at import time. Because of these benefits, the plan was to make stringified type hints the default in Python 3.10 and later 3.11, but libraries like FastAPI and Pydantic, which process annotations at runtime, found them fragile and difficult to evaluate:
The problem however is that trying to evaluate those strings to get the real annotation objects is really hard, perhaps impossible to always do correctly. (Source)
Facing those real-world obstacles, the core team looked for a more robust design and eventually adopted PEP 649. Instead of turning annotations into strings, which might require manual evaluation, Python 3.14 now represents them as data descriptors that are evaluated only when needed, then cached. This approach avoids both eager execution and the pitfalls of stringification.
Deferred Evaluation of Annotations
As the title of PEP 649—deferred evaluation of annotations—implies, Python 3.14 still evaluates annotations for you, but only when you explicitly request them. This is perhaps best illustrated with an annotation that leads to a runtime error when evaluated:
Python 3.14
>>> def function() -> 1 / 0:
... print("Python doesn't run annotations just yet.")
...
>>> function()
Python doesn't run annotations just yet.
>>> function.__annotations__
Traceback (most recent call last):
...
def function() -> 1 / 0:
~~^~~
ZeroDivisionError: division by zero
The return type specified after the arrow symbol (->) includes an expression that would normally trigger a ZeroDivisionError. However, because Python 3.14 doesn’t evaluate type annotations until you explicitly inspect them, you can still call this function without any issues. It’s only when you access the function’s .__annotations__ attribute that you observe the expected exception.
With that being said, Python still parses your annotations to check if they’re syntactically correct. If they aren’t, you’ll receive either a gentle warning or a full-blown syntax error:
Python 3.14
>>> def syntax_warning() -> b"\N":
... print("Python parses your annotations.")
...
<python-input-2>:1: SyntaxWarning: "\N" is an invalid escape sequence.
⮑ Such sequences will not work in the future.
⮑ Did you mean "\\N"? A raw string is also an option.
>>> def syntax_error() -> "\N{unknown}":
File "<python-input-0>", line 1
def syntax_error() -> "\N{unknown}":
^^^^^^^^^^^^^
SyntaxError: (unicode error) 'unicodeescape' codec can't decode bytes
⮑ in position 0-10: unknown Unicode character name
The bytes literal b"\N" contains an invalid escape sequence, which Python currently escapes for you. On the other hand, the string literal in the next function contains an unknown Unicode character name, resulting in a syntax error. Both of these examples demonstrate that Python still parses the expressions representing annotations.
It’s worth pointing out that after Python evaluates your annotations, it puts the computed values into a cache to avoid repeating potentially expensive computations. This effect is especially noticeable when you use a recursive implementation of the Fibonacci sequence, which is notoriously inefficient:
Python 3.14
>>> def fib(n):
... print(f"Calculating fib({n})...")
... return n if n < 2 else fib(n - 2) + fib(n - 1)
...
>>> def function() -> fib(5):
... pass
...
>>> function.__annotations__
Calculating fib(5)...
Calculating fib(3)...
Calculating fib(1)...
Calculating fib(2)...
Calculating fib(0)...
Calculating fib(1)...
Calculating fib(4)...
Calculating fib(2)...
Calculating fib(0)...
Calculating fib(1)...
Calculating fib(3)...
Calculating fib(1)...
Calculating fib(2)...
Calculating fib(0)...
Calculating fib(1)...
{'return': 5}
>>> function.__annotations__
{'return': 5}
>>> function.__annotations__
{'return': 5}
The first time you access the function’s .__annotations__ attribute, Python calls fib(5), which triggers a cascade of recursive calls until the recursion begins to unwind. As you can see from the output above, there are many redundant calls to fib() with the same arguments. Fortunately, this only happens once, and subsequent reads of the annotations return the cached results.
Anyway, you should steer away from using the .__annotations__ attribute directly, which is a low-level, less stable part of the internal interface. Depending on your goal, Python 3.14 gives you better tools to obtain annotations in various formats:
annotationlib.get_annotations(): A versatile annotation introspection toolinspect.get_annotations(): A slightly less capable alias of the former for backward-compatibilitytyping.get_type_hints(): A specialized runtime type introspection tool
The first utility function offers the greatest flexibility for reading annotations. It can return stringified annotations, forward references, or evaluated values:
Python 3.14
>>> from annotationlib import Format, get_annotations
>>> from dataclasses import dataclass
>>> from typing import Any, Optional
>>> @dataclass
... class LinkedList:
... head: Node
...
>>> @dataclass
... class Node:
... value: Any
... next: Optional[Node] = None
...
>>> get_annotations(LinkedList, format=Format.STRING)
{'head': 'Node'}
>>> get_annotations(LinkedList, format=Format.FORWARDREF)
{'head': ForwardRef('Node', is_class=True, owner=<class '__main__.LinkedList'>)}
>>> get_annotations(LinkedList, format=Format.VALUE)
Traceback (most recent call last):
...
NameError: name 'Node' is not defined. Did you mean: 'None'?
Notice how your earlier linked list example works flawlessly in Python 3.14, with no need to wrap the declared types in string literals.
On the other hand, when your annotations strictly represent types, then you’ll gain more from the last function, which can handle surprising edge cases:
Python 3.14
>>> from typing import Annotated, get_type_hints
>>> def function() -> Annotated["int", "Metadata"]:
... pass
...
>>> get_type_hints(function)
{'return': <class 'int'>}
>>> get_type_hints(function, include_extras=True)
{'return': typing.Annotated[int, 'Metadata']}
>>> get_annotations(function)
{'return': typing.Annotated[ForwardRef('int', is_class=True), 'Metadata']}
The behavior described in this section finally becomes the default in Python 3.14, delivering the promised benefits without earlier drawbacks that stalled the change for years. In a nutshell, lazy annotations in Python 3.14:
- Defer evaluation until annotations are accessed, improving startup performance.
- Eliminate common pain points with forward references and circular imports.
- Provide consistent introspection through new utility functions in the standard library.
- Maintain backward compatibility while paving the way to deprecate the old future directive.
This single change brings a big payoff. Type hints are faster, safer, and easier to use, without breaking your existing code.
Note: To dive deeper into deferred evaluation of annotations, read Python 3.14: Lazy Annotations.
Performance Optimizations
Under the hood, this version focuses on making Python feel leaner and more responsive. New options like subinterpreters and free-threaded builds push parallel execution forward, while the garbage collector and interpreter internals have been tuned to reduce pauses and overhead. These optimizations won’t change how you write Python, but they can make your programs run more smoothly and scale more effectively.
Parallel Subinterpreters
If you’ve ever tried speeding up CPU-bound code in Python with threads, then you’ve probably noticed that the Global Interpreter Lock (GIL) gets in the way. Only one thread can run Python bytecode at a time, so extra threads don’t buy you true parallelism. The traditional workaround is multiprocessing. But, while processes run in parallel, they carry heavy startup and data exchange costs.
Python 3.14 introduces a third option, which was previously only available through the C API. Subinterpreters finally become practical from pure Python, and you no longer have to drop down to C.
Each subinterpreter has its own GIL and isolated state, meaning multiple interpreters can run Python code truly in parallel on different CPU cores. They’re lighter than processes but still safer than threads, since interpreters don’t share global objects by default.
To make subinterpreters easy to use, the standard library now offers an InterpreterPoolExecutor in concurrent.futures. It works just like ThreadPoolExecutor or ProcessPoolExecutor. You submit callables, and you get back results. Under the hood, each worker runs in its own interpreter, so your CPU-bound tasks scale across cores.
Here’s a simple benchmark that compares the three types of executors:
subinterpreters.py
from concurrent.futures import (
InterpreterPoolExecutor,
ProcessPoolExecutor,
ThreadPoolExecutor,
)
from time import perf_counter
MAX_VALUE = 35
NUM_VALUES = 4
NUM_WORKERS = 4
def fib(n):
return n if n < 2 else fib(n - 2) + fib(n - 1)
def compute(Pool):
t1 = perf_counter()
with Pool(max_workers=NUM_WORKERS) as pool:
list(pool.map(fib, [MAX_VALUE] * NUM_VALUES))
t2 = perf_counter()
print(f"{Pool.__name__}: {(t2 - t1):.2f}s")
if __name__ == "__main__":
compute(InterpreterPoolExecutor)
compute(ProcessPoolExecutor)
compute(ThreadPoolExecutor)
With the InterpreterPoolExecutor, each fib() call runs in a separate Python interpreter, so they can progress independently without fighting over one GIL. Results and arguments must be pickleable, since interpreters don’t share live objects. Compared to processes, subinterpreters start faster and use less memory, though you still can’t pass things like open file handles between them.
This new tool sits nicely between threads and processes:
- Threads: Best for I/O-bound work, but limited for CPU-bound tasks in regular CPython.
- Processes: Maximum isolation and compatibility, but have higher overhead.
- Interpreters: Allow true parallelism with lower overhead than processes, but have stricter isolation than threads.
In short, subinterpreters in Python 3.14 give you a lightweight way to scale CPU-heavy work across cores without the cost of processes. They’re not a silver bullet, but they open up a powerful new middle ground for parallel programming in Python.
Note: Not all extension modules are ready for multiple interpreters. Some may raise an ImportError if they assume global state. For a deeper dive into the backstory, see Python 3.12: Subinterpreters.
Free-Threaded Python
The Global Interpreter Lock (GIL) ensures that only one thread can execute Python bytecode at a time. While this design has simplified CPython’s memory management for decades, it has also been a fundamental bottleneck for CPU-bound multithreaded applications. Overcoming this limitation has been a major goal for the Python community, and Python 3.14 delivers a significant step forward.
In Python 3.13, the core team unveiled an experimental free-threaded build, a version of CPython that can run multiple threads truly in parallel by disabling the GIL. This preview allowed adventurous developers to test real multithreading speedups on multicore machines, but it came with strong caveats. It wasn’t officially supported, and performance characteristics were still evolving.
With Python 3.14, free-threaded Python has reached supported status. That means the project has met the criteria laid out in PEP 779, assuring users like you that the feature will be maintained and improved in future releases. It’s no longer an experimental side branch, but an official part of CPython’s roadmap.
Note: While optional, the GIL remains enabled by default in Python 3.14. To turn it off, you need to first compile the Python source code with the --disable-gil flag. This produces a GIL-free interpreter that lets multiple native threads run Python code at the same time. Alternatively, you can streamline the building of a free-threaded version using pyenv.
For projects that require temporary fallback or compatibility, the free-threaded build can still re-enable the GIL at runtime. This flexibility helps smooth the transition for codebases and dependencies that aren’t yet ready for a GIL-free world.
The main attraction is true parallelism, so CPU-bound programs that were previously limited to single-core execution can now benefit from multiple threads running simultaneously. Early benchmarks show impressive scaling for workloads like data processing or numerical simulations. However, there are trade-offs:
- Single-thread slowdown: Running without the GIL introduces additional locking and memory-management overhead. The core team currently targets about a 10–15 % performance penalty for single-threaded code, and up to around 20 % more memory use.
- Ecosystem compatibility: Many third-party C extension modules assume the GIL exists and will need updates or recompilation to work correctly. The new build uses a separate ABI (application binary interface) to distinguish GIL-free extensions, so some compiled packages may not work out of the box.
Free-threaded Python is one of the most significant shifts in CPython’s history. It finally opens the door to true multicore performance for pure Python code, reducing the need for cumbersome workarounds or offloading heavy computations to external libraries. While it’ll take time for the broader Python ecosystem to fully embrace it, Python 3.14 provides a stable foundation for a future without the GIL.
Experimental JIT Builds
The just-in-time compiler introduced in the previous release remains experimental in Python 3.14. The JIT can translate frequently executed portions of Python bytecode into native machine instructions at runtime, potentially speeding up execution by cutting out repeated interpretation overhead. While this idea has proven effective in projects like PyPy, CPython’s JIT is still in its infancy and isn’t ready for production use.
The key change in this release is broader distribution support. On Windows and macOS, the official binary installers now include JIT-enabled builds by default, though the JIT remains turned off unless you explicitly activate it, for example, by setting the PYTHON_JIT=1 environment variable. On Linux, you still need to compile Python yourself with the --enable-experimental-jit configuration flag.
If you’re using pyenv, enabling the JIT is as simple as setting the appropriate environment variable before installation:
$ export PYTHON_CONFIGURE_OPTS='--enable-experimental-jit'
$ pyenv install 3.14.0
Once installed, Python gives you an introspection API through the new sys._jit module, which lets you check the JIT’s availability and status at runtime:
jit_status.py
try:
from sys import _jit
except ImportError:
print("Module sys._jit unavailable")
else:
print("Python compiled with JIT support:", _jit.is_available())
print("JIT enabled for this process:", _jit.is_enabled())
print("JIT currently running:", _jit.is_active())
Note the leading underscore in the module name, which hints at it being an internal interface that may change or even disappear in future releases. This small API is designed mainly for diagnostics and experimentation:
$ python3.13 main.py
Module sys._jit unavailable
$ python3.14 main.py
Python compiled with the JIT support: False
JIT enabled for this process: False
JIT currently running: False
$ python3.14-jit main.py
Python compiled with the JIT support: True
JIT enabled for this process: True
JIT currently running: False
$ PYTHON_JIT=0 python3.14-jit main.py
Python compiled with the JIT support: True
JIT enabled for this process: False
JIT currently running: False
At this stage, the JIT isn’t expected to provide consistent performance benefits. In fact, depending on your workload, it may even slow things down. The Python core team recommends treating it as an experimental playground for curious developers who want to explore the future of Python performance.
If you’re interested in low-level interpreter mechanics, the JIT is a fascinating area to watch, but for production code, you should stick with the standard interpreter for now.
Tail-Calling Interpreter
Python 3.14 introduces an alternative interpreter mode built around tail calls at the C-level. Instead of a monolithic dispatch loop, CPython can compile opcode handlers as small functions that tail-call the next handler. This tail-calling interpreter is not enabled by default. You must build CPython with the --with-tail-call-interp configuration flag to use it.
If your compiler supports guaranteed tail calls—currently Clang 19+ on x86-64 and AArch64—this design can reduce dispatch overhead and improve performance modestly in many workloads. Early benchmarks claimed 9-–15 percent improvement over older builds, though later analysis suggests more realistic gains of 3–-5 percent, adjusting for known compiler bugs.
Importantly, this is entirely internal to CPython. It doesn’t change Python’s recursion semantics, nor does it provide user-level tail recursion elimination. Your existing recursive code still hits the recursion limit as before. Also, some build combinations—for example, mixing --with-tail-call-interp and --enable-pystats—currently trigger build failures.
In short, the tail-calling interpreter in Python 3.14 is a low-level performance experiment. If your environment supports it, you may see a small speedup, but your Python code and algorithms don’t need to change, and recursion remains as before.
Incremental Garbage Collector
Python has had automatic memory management to keep your programs from running out of memory. This mechanism relies on reference counting, which quickly reclaims most objects. Additionally, Python uses garbage collection to deal with trickier cases like reference cycles. A cycle is formed when two objects reference each other, for example, keeping their reference counts above zero even when no variables point to them any longer.
Up until now, when the cycle detector kicked in, it would try to do its entire cleanup at once, which could freeze your program for a brief moment if many objects piled up. Python 3.14 changes that. Instead of sweeping everything in one go, it spreads the work across multiple steps or increments. This means shorter pauses that are barely noticeable, even under heavy workloads.
In Python 3.13, a similar feature briefly landed but was rolled back late in the release cycle after it caused unexpected performance regressions. The idea wasn’t abandoned, though. It was refined, tested further, and finally shipped in Python 3.14. This means you’re now getting the smoother experience that was originally planned, without the earlier downsides.
This change is largely transparent. Python automatically uses incremental collection now. For most developers, the improvement will be silent, but the end result should be a smoother runtime experience. It’s something you’ll especially appreciate in latency-sensitive code like servers, games, or interactive applications.
So, Should You Upgrade to Python 3.14?
If you’re already using Python 3.13, then moving to 3.14 is an easy win. The new REPL features, clearer error messages, and safer debugging tools make daily development smoother. On top of that, performance gains from subinterpreters, free-threaded builds, and an improved garbage collector lay the groundwork for faster, more scalable applications.
That said, you don’t need to rush. While most changes are backward-compatible and your existing code should run without modification, third-party libraries may need time to catch up with the new features. If your project depends heavily on C extensions, compiled wheels, or other low-level integrations, then you may want to hold off until your dependencies officially support Python 3.14.
For production environments, especially in corporate or legacy systems, stability usually outweighs shiny new features. Large organizations often prefer to wait for the first maintenance release, like 3.14.1, or even a long-term support (LTS) distribution before rolling out an upgrade across servers. This helps avoid surprises from edge cases or ecosystem incompatibilities.
On the other hand, if you’re building new projects, experimenting with concurrency, or working in environments where developer productivity is a top priority, then upgrading early makes sense. You’ll gain immediate benefits from the friendlier REPL, smarter error messages, and safer debugging tools, while positioning your codebase to take advantage of Python’s evolving parallelism story.
In short, upgrade now if you want the latest improvements and are confident in your dependency stack. Otherwise, if your priority is long-term stability in a conservative production setup, then wait until the ecosystem fully embraces the changes.
Conclusion
Every new Python release is a chance to reflect on how far the language has come and to thank the countless contributors who keep pushing it forward. With Python 3.14, you get a release that balances polish with progress, smoothing rough edges while also planting seeds for the future.
In this tutorial, you’ve seen highlights like:
- A more colorful REPL with syntax highlighting and smarter imports
- Friendlier error messages that guide you toward fixes
- A standardized, safe way to connect external debuggers
- Template strings (t-strings) for safer string interpolation
- Deferred evaluation of annotations that removes long-standing typing pain points
- Subinterpreters, a free-threaded build, and incremental garbage collection
If you’re eager to dive deeper, then check out the dedicated tutorials that zoom in on individual features:
- Python 3.14: Template Strings (T-Strings)
- Python 3.14: Lazy Annotations
- Python 3.14: REPL Autocompletion and Highlighting
- Python 3.14: Better Syntax Error Messages
Even if your projects won’t use all these features right away, installing Python 3.14 and giving them a try is the best way to get comfortable with where the language is headed. Who knows—your next side project might be the perfect place to experiment.
Get Your Code: Click here to download the free sample code that you’ll use to learn about the new features in Python 3.14.
Frequently Asked Questions
Now that you have some experience with Python 3.14 features, you can use the questions and answers below to check your understanding and recap what you’ve learned.
These FAQs are related to the most important concepts you’ve covered in this tutorial. Click the Show/Hide toggle beside each question to reveal the answer.
You create a t-string with the t prefix and get a string.templatelib.Template instead of a plain str. You use them when you want to validate or sanitize interpolations before rendering, while remembering that placeholders still evaluate eagerly unless you wrap the literal in a function.
You read annotations on demand with annotationlib.get_annotations() or typing.get_type_hints(). You choose formats like strings, forward references, or evaluated values, and Python caches results after first access, so you avoid repeated work.
You use subinterpreters when you want true parallelism for CPU-bound tasks with lower overhead than processes and better isolation than threads. You submit work with concurrent.futures.InterpreterPoolExecutor and pass only pickleable data between interpreters.
Take the Quiz: Test your knowledge with our interactive “Python 3.14: Cool New Features for You to Try” quiz. You’ll receive a score upon completion to help you track your learning progress:
Interactive Quiz
Python 3.14: Cool New Features for You to TryIn this quiz, you'll test your understanding of the new features introduced in Python 3.14. By working through this quiz, you'll review the key updates and improvements in this version of Python.







