interpreter
The Python interpreter is the program that reads and executes Python code. It serves as both a translator and a runtime environment, converting Python code (a high-level language) into machine code that your computer can execute.
The Python interpreter includes both the core execution engine and the Python Virtual Machine (VM), which provides a layer of abstraction between your code and the computer’s hardware. The reference implementation of the Python interpreter is CPython, written in the C programming language.
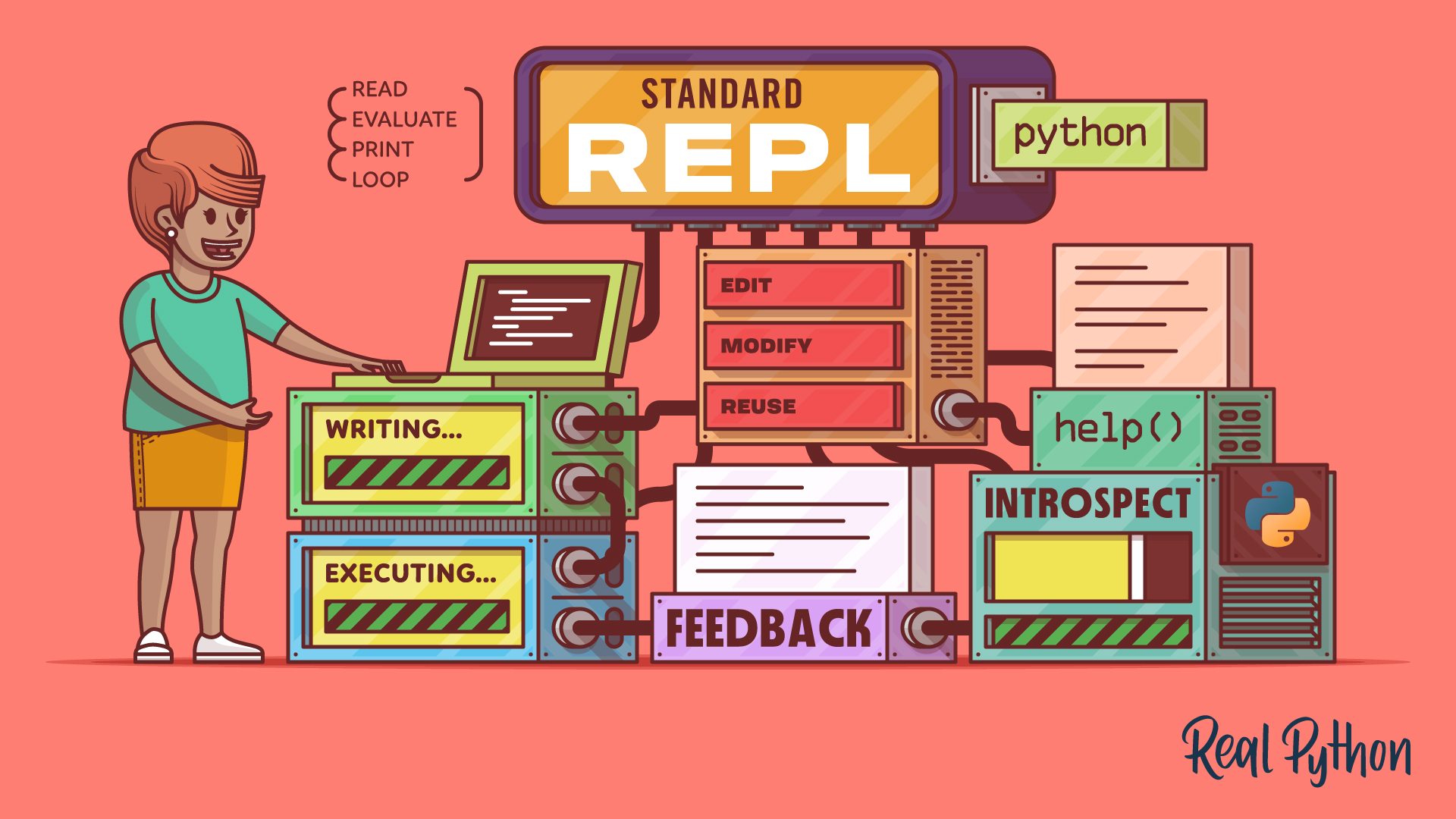
Python interpreters typically include a REPL mode that allows you to interactively test small code snippets.
Related Resources
Tutorial
The Python Standard REPL: Try Out Code and Ideas Quickly
The Python REPL gives you instant feedback as you code. Learn to use this powerful tool to type, run, debug, edit, and explore Python interactively.
For additional information on related topics, take a look at the following resources:
- Python 3.13: A Modern REPL (Tutorial)
- Interacting With Python (Tutorial)
- Discover bpython: A Python REPL With IDE-Like Features (Tutorial)
- Getting the Most Out of the Python Standard REPL (Course)
- The Python Standard REPL: Try Out Code and Ideas Quickly (Quiz)
- Ways to Start Interacting With Python (Course)
- Interacting With Python (Quiz)
- Using the bpython Enhanced REPL (Course)