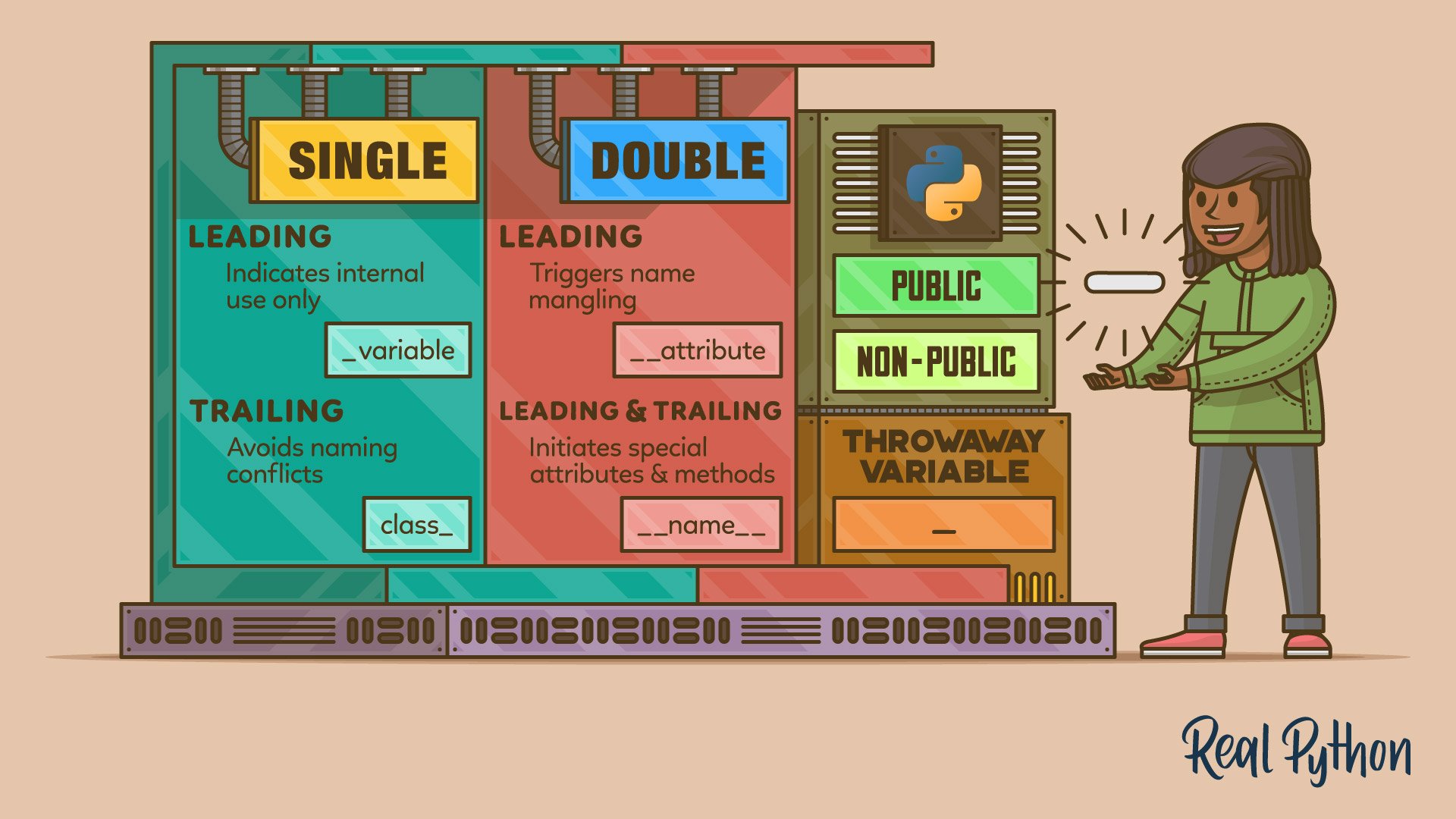
non-public name
In Python, a non-public name refers to the name of a variable, function, method, or attribute that’s intended for internal use within a module or a class. These names are prefixed with an underscore (_) to signal that you shouldn’t access or modify them directly from outside the module or class.
Python doesn’t enforce strict access restrictions. Using a leading underscore is a naming convention that indicates the intended use of certain elements.
By marking a name as non-public, you indicate that the name is an implementation detail that may change in the future and isn’t intended to be used as part of the code’s public interface.
Example
Here’s an example of non-public names in a Python class:
class DemoClass:
def __init__(self, value):
self._hidden_value = value # Non-public attribute
def get_value(self):
return self._hidden_value
# Usage
demo = DemoClass(42)
demo.get_value() # Output: 42
# Don't do this
print(demo._hidden_value) # Outputs: 42
Related Resources
Tutorial
Single and Double Underscores in Python Names
Learn Python naming conventions with single and double underscores to design APIs, create safe classes, and prevent name clashes.
For additional information on related topics, take a look at the following resources:
- Python Classes: The Power of Object-Oriented Programming (Tutorial)
- Single and Double Underscore Naming Conventions in Python (Course)
- Single and Double Underscores in Python Names (Quiz)
- Inheritance and Internals: Object-Oriented Programming in Python (Course)
- Class Concepts: Object-Oriented Programming in Python (Course)
- Python Classes - The Power of Object-Oriented Programming (Quiz)