and
In Python, the and keyword is a logical operator used to combine two Boolean expressions and return a truthy value if both expressions are true. If the left-hand expression is false, then and returns its value. Otherwise, it returns the value of the right-hand expression.
Python and Keyword Examples
Here are some quick examples to illustrate how the and keyword works:
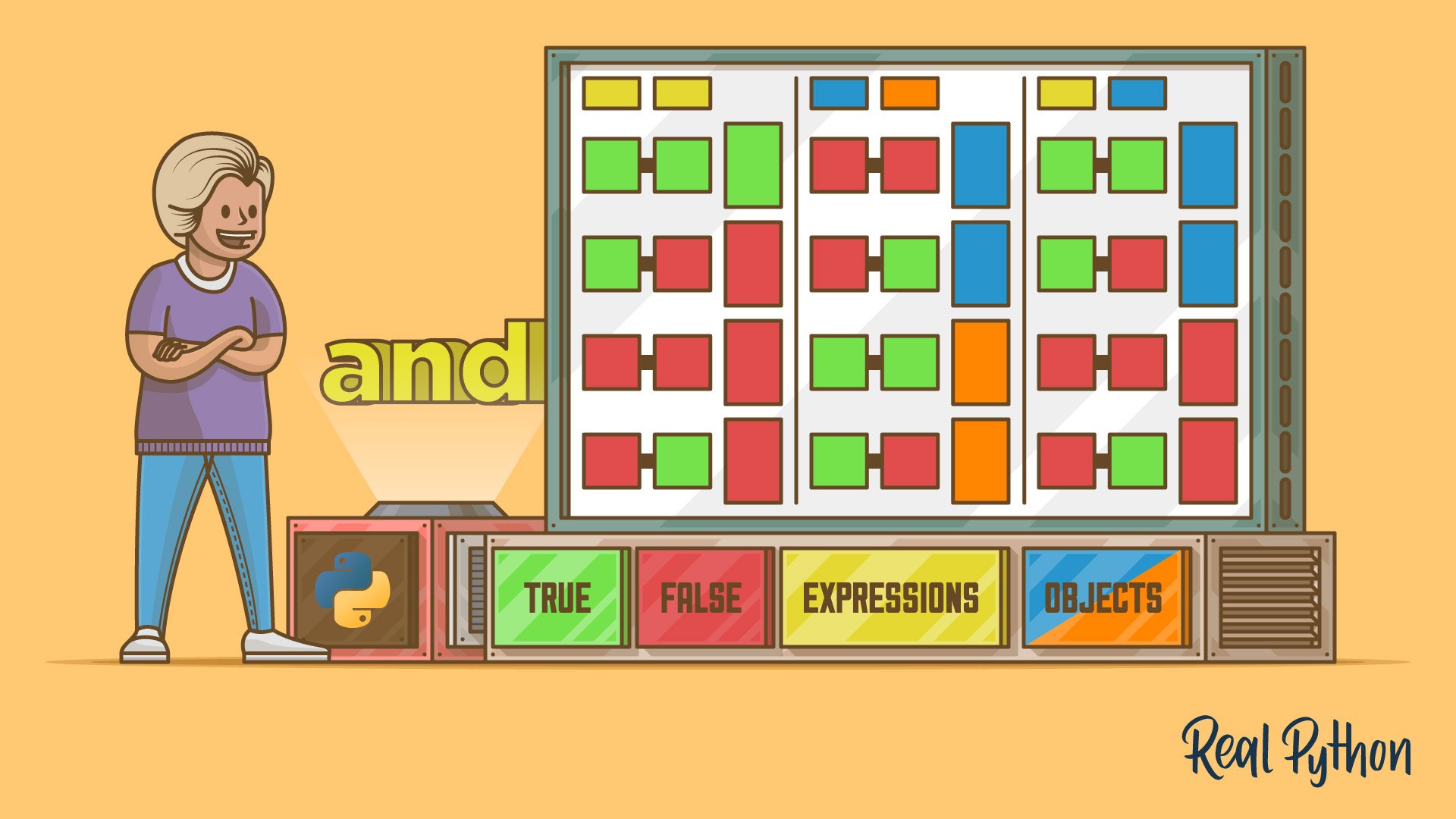
>>> True and True
True
>>> True and False
False
>>> False and True
False
>>> False and False
False
>>> 5 > 3 and 2 < 4
True
>>> 5 > 3 and 2 > 4
False
>>> "Hi!" and []
[]
>>> "Hi!" and [1, 2, 3]
[1, 2, 3]
>>> 0 and [1, 2, 3]
0
The first four examples show the truth table for the and operator. Then, you have comparison expressions combined with and. Their result is True if both expressions evaluate to True, and False otherwise.
In the last set of examples, you use and to combine objects. In each expression, you get a specific object. Note that in these examples, you don’t get True or False.
Python and Keyword Use Cases
- Combining multiple conditions in
ifstatements to execute code only if all conditions are met - Filtering data in list comprehensions and generator expressions by applying multiple criteria
- Short-circuit evaluation, where the second condition is evaluated only if the first one is true
Related Resources
Tutorial
Using the "and" Boolean Operator in Python
In this step-by-step tutorial, you'll learn how Python's "and" operator works and how to use it in your code. You'll get to know its special features and see what kind of programming problems you can solve by using "and" in Python.
For additional information on related topics, take a look at the following resources:
- Python Booleans: Use Truth Values in Your Code (Tutorial)
- Conditional Statements in Python (Tutorial)
- Using the Python and Operator (Course)
- Python Booleans: Leveraging the Values of Truth (Course)
- Conditional Statements in Python (if/elif/else) (Course)
- Python Conditional Statements (Quiz)